How CRM Prevents Data Breaches In The USA: A Comprehensive Guide
“How CRM Prevents Data Breaches in the USA: A Comprehensive Guide
How CRM Prevents Data Breaches in the USA: A Comprehensive Guide
Data breaches are a significant threat to businesses in the USA, resulting in hefty fines, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. The increasing reliance on digital technologies and the proliferation of sensitive customer data have made organizations prime targets for cybercriminals. A robust Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system, however, can play a crucial role in preventing these breaches and mitigating their impact. This article delves into the multifaceted ways a well-implemented CRM system contributes to enhanced data security in the US context.
1. Centralized Data Management: The Foundation of Data Security
One of the primary ways a CRM system prevents data breaches is through centralized data management. Unlike disparate spreadsheets and fragmented databases, a CRM consolidates all customer information – contact details, purchase history, communication logs, and more – into a single, secure platform. This centralization simplifies data access control, making it easier to implement robust security measures and monitor user activity. By eliminating the need for multiple data silos, the risk of data leakage due to accidental exposure or unauthorized access is significantly reduced. The streamlined data flow also improves the efficiency of data backups and disaster recovery planning, crucial elements in mitigating the impact of a potential breach. The US healthcare industry, for instance, with its stringent HIPAA compliance requirements, benefits immensely from the centralized data management capabilities of a CRM, ensuring patient data is securely stored and accessed only by authorized personnel. This centralization is a cornerstone of compliance and reduces the risk of hefty fines associated with data breaches under regulations like HIPAA and CCPA.
2. Access Control and User Permissions: Limiting Exposure to Sensitive Information
Effective access control is paramount in preventing data breaches. A well-configured CRM system allows administrators to assign granular user permissions, ensuring that each employee only has access to the data necessary for their role. This principle of least privilege significantly limits the potential damage caused by a compromised account. For example, a sales representative might only have access to customer contact information and purchase history, while a marketing manager might have access to broader customer segmentation data but not sensitive financial information. This layered approach minimizes the impact of a potential breach, as even if one account is compromised, the attacker’s access is limited to a specific subset of data. This granular control is vital for organizations in the US financial sector, where stringent regulations necessitate meticulous control over customer financial data to prevent identity theft and financial fraud. The implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) further strengthens access control, adding an extra layer of security beyond simple passwords.
3. Data Encryption: Protecting Data at Rest and in Transit
Data encryption is a critical security measure that protects data both when it’s stored (at rest) and when it’s being transmitted (in transit). A robust CRM system will employ strong encryption algorithms to safeguard customer data from unauthorized access, even if the system is compromised. This encryption renders the data unreadable without the correct decryption key, making it significantly harder for attackers to exploit stolen data. Many reputable CRM platforms offer end-to-end encryption, ensuring that data is encrypted throughout its lifecycle. This is especially crucial for businesses handling sensitive personal information, such as credit card details or medical records, as mandated by regulations like PCI DSS and HIPAA in the US. The use of HTTPS protocols for data transmission further enhances security, protecting data from interception during transit. Investing in a CRM with robust encryption capabilities is a proactive measure that significantly reduces the likelihood and impact of a data breach.
4. Regular Data Backups and Disaster Recovery Planning: Minimizing Downtime and Data Loss
Regular data backups are essential for business continuity and data recovery in the event of a data breach or other unforeseen circumstances. A CRM system should facilitate automated backups to a secure offsite location, allowing for quick restoration of data in case of a system failure or a malicious attack. A comprehensive disaster recovery plan, outlining procedures for data restoration and business continuity, is equally crucial. This plan should be regularly tested and updated to ensure its effectiveness in a real-world scenario. The US legal sector, for example, relies heavily on the integrity of client data. Regular backups and a robust disaster recovery plan ensure that legal documents and sensitive client information are protected from loss or corruption, minimizing disruption to operations and legal proceedings. This preparedness is not only crucial for business continuity but also for maintaining client trust and complying with legal and ethical obligations.
5. Audit Trails and Monitoring: Detecting and Responding to Suspicious Activity
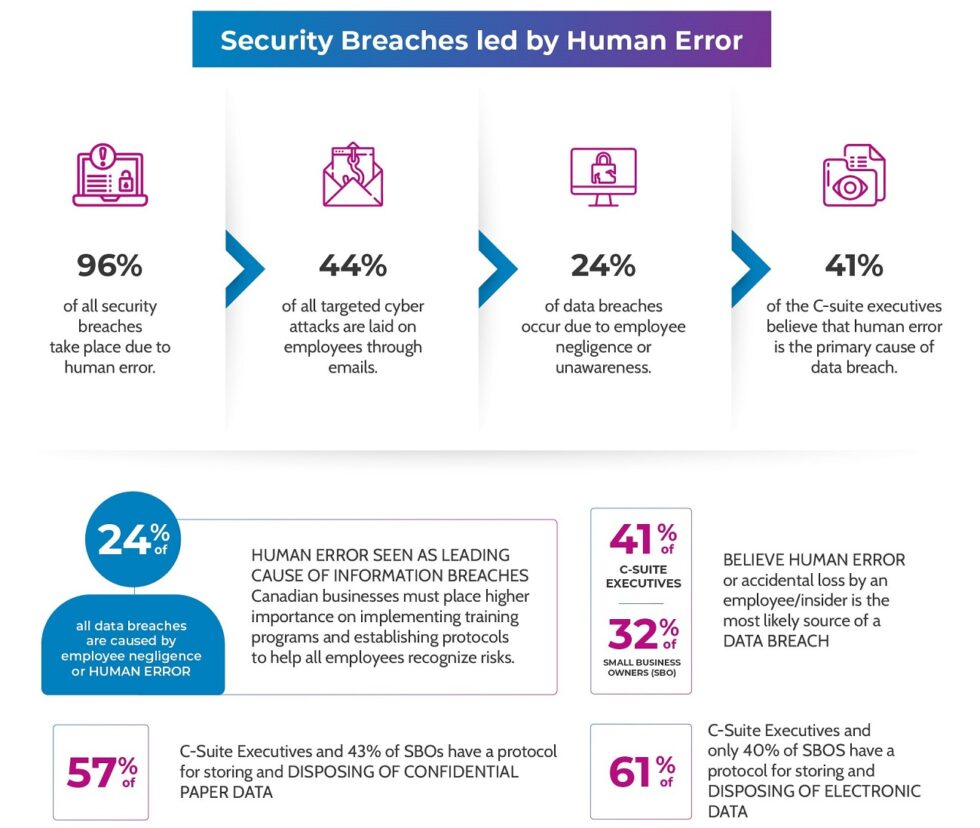
A sophisticated CRM system provides detailed audit trails, recording all user activity within the system. This logging capability allows administrators to monitor user behavior, detect suspicious activity, and identify potential security breaches early on. Real-time monitoring tools can further enhance security by alerting administrators to unusual patterns or access attempts, enabling prompt investigation and mitigation. These features are vital for proactively identifying and responding to potential threats, minimizing the impact of any security incidents. The ability to track data access and modifications is particularly important in regulated industries in the USA, allowing organizations to demonstrate compliance with regulations and provide evidence of their security practices in the event of an audit or investigation. This proactive approach to security significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and strengthens an organization’s overall security posture.
6. Regular Security Updates and Patch Management: Staying Ahead of Emerging Threats
Cybersecurity is a constantly evolving landscape, with new threats emerging regularly. A key aspect of preventing data breaches is staying up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates for the CRM system and its underlying infrastructure. Regular software updates address known vulnerabilities, reducing the attack surface and preventing exploitation by malicious actors. A proactive approach to patch management, coupled with regular security audits and penetration testing, is crucial for maintaining a strong security posture. In the US, regulatory bodies often mandate regular security assessments and updates, particularly for organizations handling sensitive personal data. Ignoring these updates can lead to significant vulnerabilities, increasing the risk of a data breach and potential legal repercussions. By prioritizing regular updates and proactively addressing security vulnerabilities, organizations can significantly reduce their risk profile and ensure the ongoing protection of their valuable customer data.
In conclusion, a well-implemented CRM system offers a robust defense against data breaches in the USA. By centralizing data, controlling access, encrypting data, implementing regular backups, monitoring activity, and staying up-to-date with security patches, organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to cyberattacks. Investing in a secure CRM is not merely a cost; it’s a strategic investment in protecting valuable customer data, maintaining compliance, and safeguarding the organization’s reputation and financial stability. The proactive measures outlined above are essential for organizations of all sizes in the US to navigate the complex landscape of data security and ensure the long-term protection of their customer information.