CRM Risk Management For USA Enterprises: A Comprehensive Guide
“CRM Risk Management for USA Enterprises: A Comprehensive Guide
CRM Risk Management for USA Enterprises: A Comprehensive Guide
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are the backbone of many US enterprises, providing invaluable insights into customer behavior and facilitating efficient sales and marketing processes. However, the reliance on CRM systems also introduces significant risks that can severely impact an organization’s bottom line, reputation, and even its survival. Effective CRM risk management is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses operating in the competitive US market. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and mitigating these risks.
1. Data Breaches and Cybersecurity Threats: The Biggest CRM Risk
Data breaches represent the most significant threat to US enterprises utilizing CRM systems. The sensitive customer data stored within these systems – including Personally Identifiable Information (PII), financial details, and purchasing history – is a lucrative target for cybercriminals. A successful breach can lead to hefty financial penalties under regulations like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), even if the business isn’t directly based in Europe. Furthermore, reputational damage from a data breach can be devastating, leading to customer churn and loss of trust. The cost of recovering from a data breach can run into millions of dollars, including legal fees, remediation efforts, and the cost of notifying affected individuals.
Keywords: CRM data breach, cybersecurity risks, CCPA compliance, GDPR compliance, data loss prevention, ransomware attacks, identity theft, data breach response plan, cybersecurity insurance.
Mitigation Strategies: Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is paramount. This includes:
- Strong password policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA): Restricting access and ensuring only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
- Regular security audits and penetration testing: Identifying vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them.
- Data encryption both in transit and at rest: Protecting data even if a breach occurs.
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS): Monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Employee cybersecurity training: Educating employees about phishing scams, malware, and other social engineering tactics.
- Regular software updates and patching: Addressing known vulnerabilities promptly.
- Data loss prevention (DLP) tools: Preventing sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network unauthorized.
- Incident response plan: Having a well-defined plan in place to respond to a data breach effectively and efficiently.
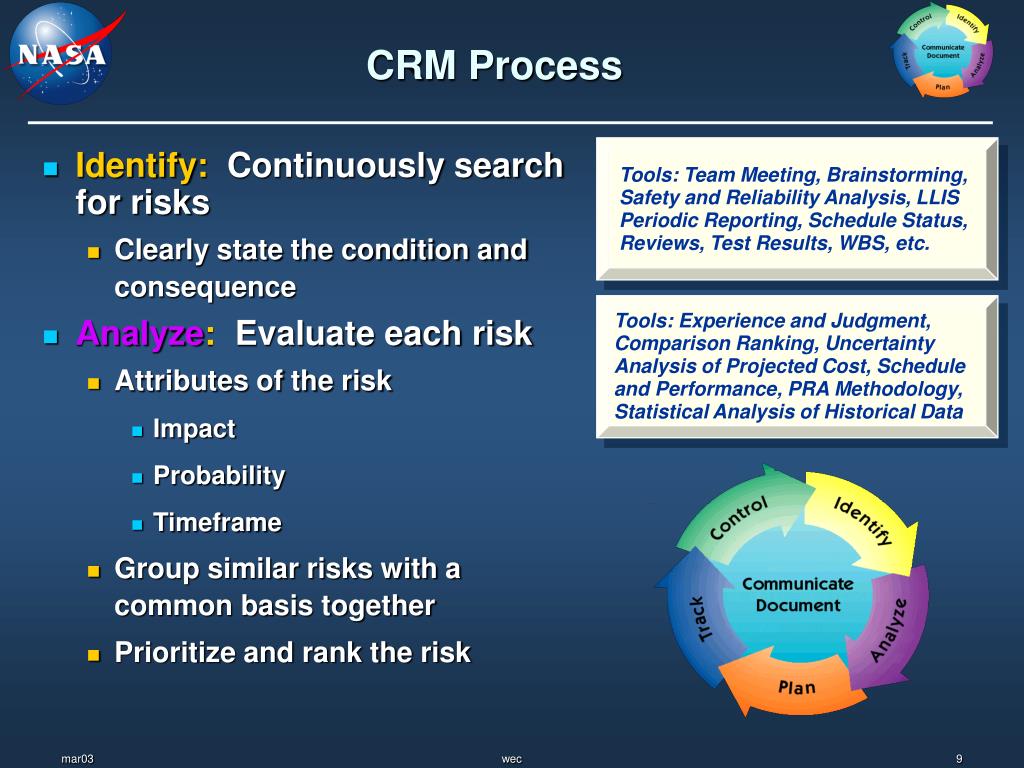
2. Data Integrity and Accuracy: Ensuring Reliable Information
Maintaining the accuracy and integrity of data within the CRM system is critical for effective decision-making. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed marketing campaigns, missed sales opportunities, and poor customer service. For example, incorrect contact information can result in failed marketing email campaigns and wasted marketing budget. Inaccurate customer segmentation can lead to irrelevant marketing messages and frustrated customers.
Keywords: Data quality, data cleansing, data validation, CRM data accuracy, data governance, CRM integration, data migration risks, master data management.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Data cleansing and validation processes: Regularly reviewing and cleaning data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Data governance policies and procedures: Establishing clear guidelines for data entry, updates, and maintenance.
- Data quality monitoring tools: Tracking data quality metrics and identifying areas for improvement.
- Regular data backups and recovery procedures: Ensuring data can be restored in case of data loss or corruption.
- Integration with other systems: Ensuring seamless data flow between the CRM and other business systems to minimize data inconsistencies.
- Master Data Management (MDM) solutions: Implementing a centralized system for managing critical data elements across the organization.
3. Vendor Risk Management: Choosing and Managing CRM Providers
Choosing the right CRM vendor is crucial, and the selection process should include a thorough assessment of the vendor’s security practices, data protection policies, and service level agreements (SLAs). Selecting a vendor with a poor security track record can expose your organization to significant risk. Ongoing monitoring of the vendor’s performance and adherence to SLAs is also essential.
Keywords: CRM vendor selection, vendor risk assessment, service level agreements (SLAs), cloud security, SaaS security, vendor due diligence, third-party risk management.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Conduct thorough due diligence: Carefully evaluate potential vendors based on security certifications, compliance with relevant regulations, and customer references.
- Negotiate robust SLAs: Clearly define the vendor’s responsibilities regarding security, uptime, and data protection.
- Regularly monitor vendor performance: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) to ensure the vendor is meeting its obligations.
- Establish clear communication channels: Maintain open communication with the vendor to address any concerns or issues promptly.
- Develop an exit strategy: Have a plan in place for transitioning to a new vendor if necessary.
4. User Error and Misuse: Human Factors in CRM Risk
Human error is a significant source of CRM risk. Employees may accidentally delete important data, enter inaccurate information, or fail to follow security protocols. Malicious insiders can also pose a threat, intentionally misusing the CRM system for personal gain or to damage the organization.
Keywords: Human error, insider threats, access control, role-based access control (RBAC), employee training, security awareness training, data loss prevention (DLP).
Mitigation Strategies:
- Implement robust access controls: Restricting access to sensitive data based on roles and responsibilities.
- Provide comprehensive employee training: Educating employees on proper CRM usage, security protocols, and data handling procedures.
- Regularly monitor user activity: Detecting suspicious behavior and potential misuse of the system.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC): Granting users only the necessary permissions to perform their jobs.
- Establish clear policies and procedures: Defining acceptable use of the CRM system and the consequences of violating these policies.
5. Integration Risks: Connecting CRM to Other Systems
Integrating the CRM system with other business systems, such as ERP or marketing automation platforms, can improve efficiency and data flow. However, poor integration can introduce new risks, such as data inconsistencies, security vulnerabilities, and performance issues.
Keywords: CRM integration risks, data synchronization, API security, application programming interface (API), system integration testing, data mapping, enterprise resource planning (ERP) integration, marketing automation integration.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Thoroughly test integrations: Conduct rigorous testing to ensure data integrity and system compatibility.
- Secure APIs: Implement robust security measures to protect data transmitted between systems.
- Develop a comprehensive integration plan: Clearly define the scope, objectives, and timelines for integration projects.
- Monitor integration performance: Track key metrics to identify and address any performance issues.
- Establish clear data mapping rules: Defining how data will be transferred between systems to ensure consistency.
6. Regulatory Compliance and Legal Risks: Navigating the Legal Landscape
US enterprises must comply with various federal and state regulations regarding data privacy, security, and consumer protection. Failure to comply can result in significant fines, legal action, and reputational damage. Regulations such as CCPA, HIPAA (for healthcare data), and GLBA (for financial data) all impact CRM usage.
Keywords: Data privacy regulations, CCPA compliance, HIPAA compliance, GLBA compliance, regulatory compliance, legal risk management, data breach notification laws, privacy policy.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Stay informed about relevant regulations: Keep abreast of changes in data privacy and security laws.
- Develop a comprehensive compliance program: Implementing policies, procedures, and controls to ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
- Conduct regular compliance audits: Assessing the effectiveness of compliance programs and identifying areas for improvement.
- Implement data governance policies: Establishing clear guidelines for data collection, use, and retention.
- Maintain accurate records of compliance activities: Documenting compliance efforts to demonstrate adherence to regulations.
By proactively addressing these risks through robust risk management strategies, US enterprises can leverage the power of CRM systems while minimizing potential disruptions and maximizing the return on investment. Remember that CRM risk management is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, adaptation, and improvement to stay ahead of evolving threats and regulations.